
Image compression is the process of reducing file sizes without significantly affecting quality, important for efficient storage and faster digital performance. There are two primary categories for data compression methods. One approach maintains the original quality without any loss. The other approach sacrifices some quality to accomplish higher compression levels. Popular formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF suit different needs, with JPEG ideal for photos, PNG for high-quality images, and GIF for simple animations. Programs like Adobe Photoshop and websites like TinyPNG help make image files smaller. Grasping methods such as batch processing and data preparation boosts efficiency & results. Discover more to effectively optimize image management practices.
Key Takeaways
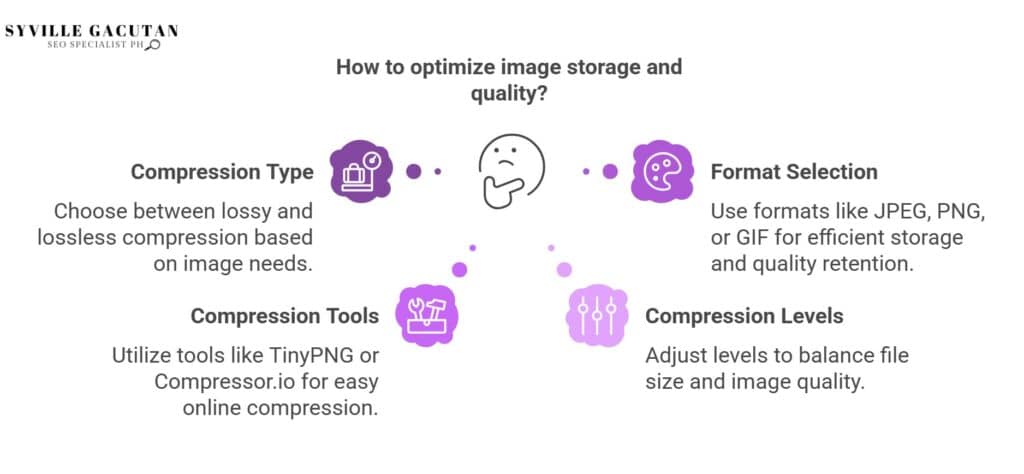
- Understand the difference between lossy and lossless compression to choose the best method for your image needs.
- Familiarize yourself with common formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF for efficient image storage and quality retention.
- Use tools like TinyPNG or Compressor.io for easy online image compression without needing advanced software.
- Learn to adjust compression levels to balance between file size reduction and maintaining acceptable image quality.
- Explore batch processing features to automate repetitive tasks and enhance productivity in image management workflows.
Understanding Image Compression
Shrinking image file sizes is vital for digital content. It allows smaller files without major quality loss. This process is vital for efficient storage and transmission of digital images, particularly in an era where high-resolution images are ubiquitous. Understanding what image compression means is essential for anyone working with digital media. The process involves applying different compression methods to encode information in a more efficient way decreasing the data needed to represent an image.
There are two primary types of compression: lossless and lossy. Lossless compression is a method that reduces file size without any loss of quality. This technique is particularly useful for applications where the integrity of the image is paramount, such as in medical imaging or technical drawings. Compression methods like PNG & GIF formats allow the original information to be rebuilt perfectly from the compressed version. These techniques do not lose any data during the compression process.
The process of image compression is not just about reducing file size but also about making digital images more manageable and less taxing on storage and bandwidth. Various compression techniques, such as Run-Length Encoding and Huffman Coding, are employed to achieve this.
Those techniques function by removing unnecessary repetitions present in the image information. This process enables more efficient storage utilization.
Benefits of Compressing Images

Compressing images offers numerous advantages that are particularly relevant in today’s digital landscape. As the demand for digital content continues to grow, the ability to compress images effectively has become an essential skill. One of the foremost benefits of compressing images is the significant reduction in file size, which facilitates faster loading times on web pages and improved performance in digital applications. This is especially crucial for enhancing user experience on mobile devices, where bandwidth may be limited.
Moreover, compressing images can lead to more efficient storage solutions. By reducing the file size, businesses and individuals can save valuable space on servers, cloud storage, and personal devices. This reduction not only lowers costs associated with storage but also contributes to a more streamlined data management process.
Importantly, while compressing images, it is possible to maintain a high level of image quality through techniques such as lossless compression. This method ensures that the original data can be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data, preserving the integrity and clarity of the image. As a result, users can achieve optimal balance between reduced file size and maintained image quality, meeting both the aesthetic and functional needs of digital content.
Furthermore, the benefits of compressing images extend beyond mere technical advantages. For businesses, it can enhance customer satisfaction by providing a seamless browsing experience, and for content creators, it can ensure their work reaches a wider audience by accommodating various device capabilities.
Ultimately, mastering image compression is a strategic move in optimizing digital content for today’s fast-paced, information-driven world.
Lossy Vs Lossless Compression
Understanding the differences between lossy and lossless compression techniques is fundamental when considering the balance between image quality and file size reduction. These two approaches cater to different needs and outcomes, depending on the intended use of the images.
Lossy compression, as the name suggests, involves some loss of data and detail from the original image. This type of compression algorithm is designed to reduce file size significantly, often resulting in a higher compression rate. Commonly used in image file types like JPEG, lossy compression is suitable for situations where reduced file size is more critical than retaining every detail, such as in web images or social media posts.
In contrast, lossless compression maintains the original image data, allowing for exact reconstruction of the original file without losing any detail. This is achieved through a compression algorithm that reduces file size by removing redundant information without sacrificing quality. Image file types such as PNG and BMP utilize lossless compression, making them ideal for scenarios where maintaining the integrity of the image is essential, like in professional photography or graphic design projects.
Choosing between lossy and lossless compression depends largely on the specific needs of the user. If minimizing storage space or bandwidth usage is a priority, lossy compression offers a higher compression rate at the expense of some image quality. Conversely, when preserving image quality is paramount, lossless compression is preferable, despite typically resulting in larger file sizes.
Understanding these differences ensures informed decisions, optimizing both image quality and resource efficiency in various applications.
Common Image File Formats

A diverse range of image file formats exists to accommodate various needs related to quality, compression, and compatibility. Among the most common image file formats are JPEG, PNG, and GIF, each offering unique attributes tailored for different applications.
JPEG, or Joint Photographic Experts Group, is a widely used format known for its lossy compression. It is ideal for photographs and complex images that require a balance between quality and file size. JPEG compression reduces file size significantly by discarding some image data, which can result in a loss of quality that is often imperceptible to the human eye. This makes JPEG a popular choice for web use, where quick loading times are essential.
PNG, or Portable Network Graphics, is renowned for its lossless image compression capabilities. This format is perfect for images requiring transparency and high-quality detail, such as logos and line art. Unlike JPEG, PNG retains all original image data, ensuring no loss in quality. However, this results in larger file sizes, which can be a consideration for web applications where bandwidth is a concern.
GIF, short for Graphics Interchange Format, is another common image format. It supports lossless compression but is limited to a palette of 256 colors. This makes GIF suitable for simpler images, such as graphics and short animations. GIFs are widely used for animated sequences due to their ability to store multiple frames within a single file.
Understanding these common image file formats and their characteristics allows for informed decisions when selecting the appropriate format for specific image needs, balancing quality, compression, and compatibility efficiently.
Tools for Image Compression

Effective image compression is essential for optimizing digital images without sacrificing quality, and a variety of tools are available to assist in this process. These tools employ different compression methods, ranging from lossy to lossless compression, each suitable for specific needs. Choosing the appropriate image compressor can significantly impact the quality and size of the resulting files, thereby influencing storage efficiency and loading times.
One popular tool for image compression is Adobe Photoshop, which offers advanced features including both lossy and lossless compression techniques. It allows users to fine-tune the compression process, enabling them to achieve the best results tailored to their specific requirements. For instance, Photoshop’s “Save for Web” option offers control over file size and quality, which is crucial for web optimization.
Another powerful tool is GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program), an open-source alternative that provides robust capabilities for image compression. GIMP supports various file formats and possesses a range of compression methods, making it versatile for users who need flexibility without incurring costs.
For those seeking simplicity, tools like JPEGmini or PNGGauntlet offer straightforward interfaces dedicated to specific formats. JPEGmini focuses on minimizing JPEG file sizes while retaining high quality, whereas PNGGauntlet excels in compressing PNG files using lossless compression, thus ensuring no data loss.
Ultimately, selecting the right tools for image compression depends on the desired balance between image quality and file size. Understanding the strengths of each image compressor and its applicable compression method is crucial for achieving optimal results, whether for professional digital media projects or casual personal use.
Online Compression Tools

While desktop applications like Adobe Photoshop and GIMP offer robust solutions for image compression, online compression tools provide a convenient alternative for users seeking quick and accessible options. These web-based platforms are particularly beneficial for those who need to compress images without installing software, ensuring ease of use and accessibility from any device with internet connectivity.
Online compression tools are designed to efficiently process image compression tasks, allowing users to compress their images with minimal effort.
One of the key advantages of using online compression tools is their capability to handle various file types, including JPEG, PNG, and GIF. These tools often offer both lossless and lossy compression options, providing flexibility depending on the user’s needs.
Lossless image compression maintains the original quality of the image while reducing file size, making it ideal for professional use where image integrity is crucial. On the other hand, lossy compression sacrifices some quality for more significant file size reduction, which might be more suitable for web use where speed is a priority.
Furthermore, many online compression tools offer batch processing capabilities, allowing users to compress multiple images simultaneously. This feature is particularly useful for those managing large collections of images.
Notable online compression tools include TinyPNG, Compressor.io, and Kraken.io, each offering unique features such as drag-and-drop interfaces, direct cloud storage integration, and customizable compression settings.
Software for Compression

Turning to software for compression, these programs provide comprehensive solutions for users who require more control and advanced features in their image compression tasks. Unlike online tools, software for compression often offers a wider array of functionalities, suitable for professional and personal use.
By utilizing such software, users can effectively manage file size while preserving the quality of their images across various image formats. One popular method employed is the use of a lossless compression algorithm, which minimizes file size without sacrificing image integrity.
Compression means the process of reducing the file size of an image, making it easier and quicker to store and share. With the right software, users can choose different levels of compression tailored to their needs, maintaining a balance between quality and efficiency. This is especially significant in fields where high-resolution images are crucial yet storage and bandwidth are limited.
Here’s a look at some notable features you might find in software for compression:
- Batch Processing: Compress multiple images simultaneously, saving time and effort.
- Format Conversion: Convert images to other formats while compressing, ensuring compatibility and convenience.
- Advanced Settings: Fine-tune compression levels and choose between various algorithms, including lossless options.
- Preview Functionality: View changes in real-time, allowing for informed adjustments before finalizing the compression.
- Metadata Management: Retain or strip metadata, depending on privacy and file size requirements.
Selecting the right software for compression depends on individual needs and the types of images being handled. By understanding these aspects, users can effectively use software tools to optimize their image management practices.
Techniques for Maintaining Quality

When utilizing software for compression, ensuring the preservation of image quality is a primary concern for many users. Compression can make a significant difference in file size, but this should not come at the cost of the quality of the image. Understanding the difference between lossy and lossless compression is crucial.
Lossy compression reduces file size by eliminating some image content, which may result in a loss of detail. This technique is often used for types of images where perfect fidelity is not necessary, such as web graphics. Conversely, lossless compression retains all original image data, making it ideal for archival purposes where maintaining quality is paramount.
One of the effective techniques for maintaining quality during compression involves selecting the appropriate format based on the image type. For instance, PNG is a lossless format suitable for images requiring transparency or intricate details, while JPEG is a lossy format that efficiently compresses photographs where slight quality loss is less noticeable.
Additionally, adjusting the compression ratio is vital. By carefully balancing the compression level, users can minimize quality loss while achieving the desired file size.
Another technique involves image preprocessing, such as resizing or cropping before compression. Reducing the dimensions of an image can significantly decrease file size without affecting the quality of the remaining content.
Furthermore, utilizing advanced software that offers preview options can help users to visualize the impact of compression on the image quality. By employing these methods, users can ensure that image compression achieves the desired balance between reduced file size and maintained quality.
Batch Processing Images

Batch processing images is an invaluable technique for efficiently handling multiple files simultaneously. By automating the compression of numerous images, it significantly reduces the time and effort required to manage such tasks individually. This approach is especially beneficial for professionals dealing with large volumes of images, such as photographers, graphic designers, and web developers.
Through batch processing, one can apply consistent compression settings across a collection of images, ensuring uniformity in quality and file size.
When engaging in batch processing, it is crucial to consider the file format. Opting for a lossless format helps maintain the integrity of the original image while reducing file size. Formats like PNG or TIFF can be advantageous for preserving details that might be lost with more lossy options like JPEG.
However, selecting the appropriate file format depends heavily on the intended use of the images and the acceptable trade-off between quality and compression.
Here are some key benefits of batch processing images:
- Time Efficiency: Streamlines the workflow by processing hundreds of images in minutes.
- Consistency: Ensures uniform image quality and file size across all processed images.
- Flexibility: Allows for easy adjustments to compression settings according to specific needs.
- Resource Management: Frees up computer resources by automating the task without constant user intervention.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes the risk of manual errors by automating repetitive tasks.
Understanding the nuances of batch processing not only enhances productivity but also ensures that the quality of the original images is maintained, making it a pivotal aspect of modern image management.
Best Practices for Beginners

Building on the efficiency and consistency achieved through batch processing, beginners can greatly benefit from adopting best practices in image compression to enhance their workflow. Image compression can make a significant difference in storage efficiency and loading speed, especially when beginners understand how to effectively apply both lossless and lossy compression techniques. Selecting the best lossless method ensures no data is lost during compression, while lossy compression can be used to significantly reduce file sizes at the cost of some quality.
A critical practice is determining the optimal compression level for each specific use case. Over-compression can result in unacceptable quality loss, whereas under-compression fails to maximize potential savings in file size. Converting an image to an appropriate format is crucial, whether it’s JPEG for lossy compression or PNG for the best lossless results. Understanding these nuances can empower beginners to make informed decisions.
Below is a table illustrating key considerations for beginners:
| Aspect | Description |
| Compression Type | Choose between lossless and lossy methods |
| File Format | Select JPEG for lossy, PNG for lossless |
| Compression Level | Balance between file size and image quality |
| Conversion Strategy | Adapt format based on intended use |
Final Thoughts
Mastering image compression is essential for anyone working with digital content, whether you’re managing personal files or optimizing websites. By understanding the differences between lossy and lossless compression, familiarizing yourself with common formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF, and leveraging the right tools, you can efficiently reduce image file sizes without compromising quality. Implementing best practices like batch processing and adjusting compression levels will save time and ensure your images are both web-friendly and high-performing.
If you want to optimize your images for faster loading speeds and better SEO without sacrificing quality, connect with Syville Gacutan, an experienced SEO Specialist in the Philippines. Syville can help you master image compression techniques, enhance your website’s performance, and ensure your images are perfectly optimized for search engines. Don’t leave your SEO success to chance—partner with an expert who understands the power of efficient image management.