
Understanding the impact of 301 vs 302 redirects on SEO is essential for effective website management. A 301 redirect indicates a permanent move and transfers SEO value, preserving link equity and authority, making it ideal for permanent URL changes. Conversely, a 302 redirect suggests a temporary move, retaining the original URL’s ranking and link equity during the change but not transferring authority to the new URL. Misusing these can lead to SEO issues and user confusion, with 302 redirects causing potential dilution of authority if used extensively. To fully understand these redirects additional explanations are available.
Key Takeaways
- 301 redirects permanently transfer SEO value and ranking power to the new URL, preserving link equity.
- 302 redirects maintain the original URL’s ranking, signaling a temporary URL change without transferring full authority.
- Incorrect use of 302 instead of 301 can diminish SEO benefits and cause ranking loss.
- Prolonged use of 302 redirects may dilute page authority between the original and new URLs.
- 301 redirects ensure seamless user experience by minimizing disruption during URL changes.
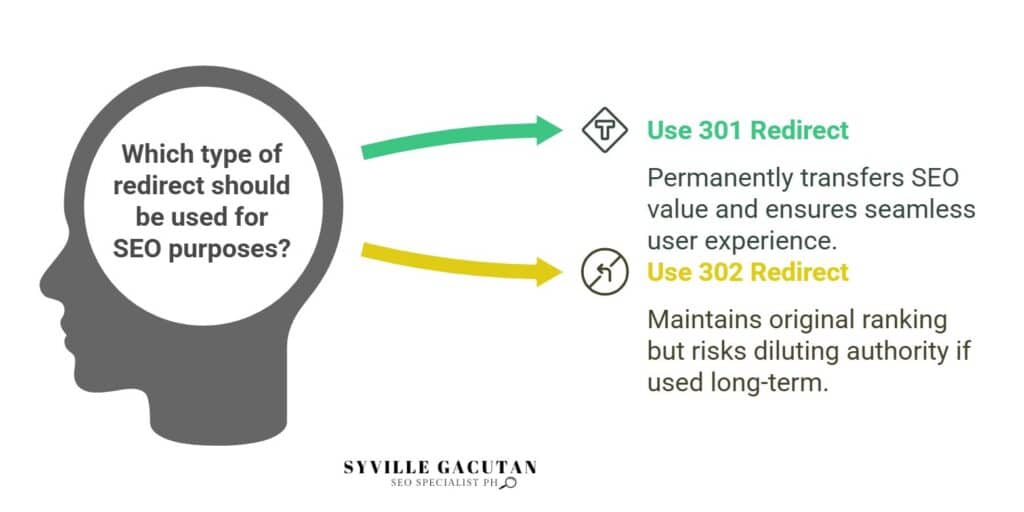
Understanding URL Redirects

URL redirects are a crucial mechanism in web development that allow users and search engines to be automatically directed from one web address to another.
These redirects ensure that visitors reach the intended content even if the URL has changed. In the realm of redirects, understanding the difference between 301 and 302 redirects is essential, as they can significantly impact your SEO strategy.
The primary distinction between 301 vs 302 redirects lies in their intended permanence. A 301 redirect is used to indicate that a webpage has been permanently moved to a new location.
It ensures that search engines transfer the SEO value from the old URL to the new one, preserving the page’s search ranking. In contrast, a 302 redirect is temporary, suggesting that the original page will return eventually.
Consequently, search engines do not transfer SEO value, which can lead to a potential loss in search ranking for the redirected page.
Using the correct redirect is critical for maintaining the SEO integrity of your website.
Implementing a 301 redirect when a 302 is appropriate, or vice versa, can lead to confusion for search engines and users alike, ultimately impacting your site’s visibility and authority.
Therefore, it’s imperative to assess the nature of the URL change to determine which type of redirect best aligns with your objectives.
Permanent Redirect: 301
A permanent redirect, known as a 301 redirect, is an essential tool in web development and SEO strategy. When a webpage is moved permanently, employing a 301 redirect ensures that both users and search engines are directed to the new URL.
Unlike a 302 redirect, which is temporary, a 301 redirect is a permanent solution, signaling search engines to update their index and transfer the ranking power of the original page to the new one. This transfer is crucial for maintaining the SEO value, as it helps preserve the accumulated search engine ranking and link equity.
From an SEO perspective, utilizing a 301 redirect is better for SEO when compared to a 302 redirect for permanent moves. 301 redirects are more effective in maintaining the authority and relevance of the webpage.
When search engines, like Google, encounter a 301 redirect, they understand that the original page has moved permanently and adjust their algorithms accordingly, which has a positive impact on SEO by ensuring the new page can inherit the old page’s search rankings.
In situations where a URL needs to be changed permanently, it is imperative to use a 301 redirect. This practice not only helps retain users by guiding them seamlessly to the new location but also assists in preserving the hard-earned SEO rankings.
In contrast, failing to employ the correct redirect type, such as incorrectly using a 302 redirect, could lead to loss of ranking and diminished visibility in search engine results.
Therefore, understanding the strategic use of 301 and 302 redirects is vital for effective SEO management.
Temporary Redirect: 302
While 301 redirects are the go-to solution for permanent changes, 302 redirects serve a different purpose by signaling a temporary change in the location of a webpage. A 302 redirect is a temporary type of redirect used when a webpage needs to be moved temporarily, without affecting the original URL‘s ranking or link equity. This makes it an ideal choice for scenarios where you anticipate that the change will not be permanent, such as during website maintenance, A/B testing, or when running short-term promotions.
Using a 302 redirect can be beneficial in maintaining your website’s SEO when you do not want to lose the search engine ranking of the original page. It essentially tells search engines that the move is temporary, and the original URL should still be indexed and included in search results. This is particularly useful for preserving the SEO health of the original page, ensuring that its authority and ranking are not transferred to the new URL.
However, it’s crucial to exercise caution, as improper use of a 302 redirect can negatively impact your SEO. If the search engines interpret the redirect as permanent due to prolonged use, it might result in the loss of ranking power for the original URL.
Therefore, it is essential to evaluate the necessity and duration of the redirect carefully. A 302 redirect should only be used when you are confident that the change is temporary and you intend to revert to the original URL in the foreseeable future. This strategy ensures that your website’s SEO remains intact during temporary changes.
SEO Impact of 301 Redirects

When a webpage undergoes a permanent change in its URL, implementing a 301 redirect is crucial for maintaining its SEO integrity. A 301 redirect signals search engines that the original URL has been permanently moved to a new location, allowing them to transfer the SEO value, including link equity, to the new URL. This process ensures that the changes do not adversely affect the website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The SEO impact of using a 301 redirect is generally positive, as it helps preserve the accumulated SEO value of the original page. By using permanent redirects, webmasters can ensure that both users and search engines are directed to the correct location without losing the traffic and authority built over time.
In contrast, a 302 redirect, which is intended for temporary changes, does not pass on the same link equity, potentially leading to a loss in ranking if used incorrectly.
Choosing between a 301 or 302 redirect depends on the nature of the URL change. For permanent changes, a 301 redirect is the preferred choice due to its ability to maintain SEO benefits.
Search engines handle these redirects differently, with 301s being a strong signal to update their index and transfer the SEO value to the new URL.
SEO Impact of 302 Redirects

Unlike a permanent 301 redirect, the 302 redirect serves as a temporary signal to search engines that a particular URL has been temporarily moved to a new location.
In the context of 301 vs 302 redirect, understanding the fundamental difference between these two types is crucial for maintaining optimal SEO performance. A 302 redirect indicates that the original URL will eventually return, and as such, search engines might not pass the same level of link equity and ranking power to the new URL as they would with a 301 redirect.
The 302 redirects impact on SEO can be significant, mainly due to its temporary nature. When you use a 302 to redirect, search engines might choose to continue indexing the original URL, assuming that the change is not permanent.
This assumption can lead to the new URL not receiving the full benefit of the original page’s authority, which could negatively impact your SEO efforts, especially if the change becomes permanent but is not updated to a 301 redirect.
Additionally, using the wrong type of redirect can lead to confusion for both users and search engines. A 302 redirect, when used incorrectly, may result in diluted page authority, as the search engine may split authority between the two URLs.
Therefore, it’s essential to assess whether the move is genuinely temporary or if a permanent solution, like a 301 redirect, would better serve your SEO objectives.
Page Authority Transfer

In the realm of search engine optimization, understanding how redirects affect page authority transfer is vital for maintaining a site’s ranking strength. The primary distinction between 301 and 302 redirects lies in their intended purpose: a 301 redirect signals a permanent move, while a 302 redirect indicates a temporary change. This distinction significantly impacts SEO performance, particularly in how link equity, or page authority, is transferred from one URL to another.
To illustrate, consider the following table that outlines the key differences:
| Redirect Type | Page Authority Transfer | SEO Performance Impact |
| 301 Redirect | Complete transfer | Enhances SEO stability |
| 302 Redirect | Limited transfer | Potential SEO disruption |
| Correct Use | Ensures optimal results | Preserves ranking power |
When employing redirects, using the correct type is crucial for ensuring the desired page authority transfer. A 301 redirect is preferred when the move is permanent, as it facilitates the full transfer of page authority, thereby preserving the SEO performance of the original page. Conversely, a 302 redirect should be reserved for temporary changes, as it only offers limited authority transfer. Misuse of 302 redirects where a 301 is warranted can lead to diminished rankings and loss of link equity.
Webmasters and SEO professionals must exercise diligence in choosing the correct redirect to maintain page authority and optimize SEO performance. By aligning the redirect type with its intended purpose, they can ensure that their site’s ranking power remains intact. This careful approach not only supports immediate SEO goals but also contributes to long-term visibility and success in search engine results.
User Experience Considerations

Understanding how redirects impact SEO goes beyond the technical aspects of page authority transfer; it also involves considering user experience, a critical factor in maintaining and improving site performance.
When users visit a website, their experience is shaped by how quickly and seamlessly they can access content. This is where the choice between 301 vs 302 redirects becomes significant. A 301 redirect is used for permanent changes, ensuring that users are automatically directed to the new page without encountering errors or delays. This approach can enhance user satisfaction by providing a smooth transition.
In contrast, a 302 redirect indicates a temporary move, which can be beneficial for short-term campaigns or seasonal content. However, frequent or improper use of 302 redirects may confuse users, as it suggests the original content will return. This could lead to frustration if the expected content is no longer available, impacting overall site engagement negatively.
To enhance user experience, it is essential to ensure that the redirect ensures minimal disruption. Slow loading times, redirect loops, or broken links can detract from user satisfaction and contribute to higher bounce rates.
Therefore, choosing the correct type of redirect for your website’s needs is crucial for maintaining your website’s SEO and ensuring a positive user experience. By understanding the 301 vs 302 redirects impact, webmasters can strategize more effectively, aligning technical SEO practices with user experience to foster a more engaging and reliable online environment.
This alignment is pivotal in retaining visitors and improving overall site performance.
Redirect Implementation Tips

Implementing redirects effectively is crucial for maintaining both SEO integrity and user experience. To ensure optimal outcomes, understanding the differences between 301 and 302 redirects is essential. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that tells search engines the original page has moved permanently, thus transferring nearly all the SEO value to the new page. On the other hand, a temporary redirect, such as a 302, indicates that the move is not permanent and the original URL may return.
When deciding whether a 301 redirect is necessary, consider the following tips:
- Use 301 redirects for permanent URL changes to consolidate link equity and maintain search engine rankings.
- When implementing a temporary redirect, ensure it is indeed temporary; otherwise, it may confuse search engines and users.
- Regularly audit existing redirects to ensure they still align with your website’s current structure and goals.
- Test redirects thoroughly after implementation to verify they resolve correctly and do not create redirect chains or loops.
Incorporating these best practices into your redirect strategy not only aids in preserving SEO value but also enhances user experience by ensuring seamless navigation.
For instance, when a 301 redirect is necessary, deploying it correctly guarantees that users and search engines are directed to the intended destination without loss of authority or relevance.
Conversely, misuse of temporary redirects can lead to diminished SEO performance if not managed properly. Therefore, a thorough understanding of when and how to use 301 redirects is paramount for any webmaster aiming to maintain an effective online presence.
Common Redirect Mistakes

Navigating the complexities of redirect management often leads to common mistakes that can undermine both SEO efforts and user experience. One prevalent error is the misuse of 301 and 302 redirects. Understanding the distinction is crucial, as using 301 and 302 incorrectly can adversely affect your website’s SEO.
A 301 redirect is a way of permanently moving a webpage, transferring most of the original page’s link equity to the new location, thus preserving SEO benefits. In contrast, a 302 redirect indicates a temporary move, which does not pass the same SEO value. Improperly implementing a 302 redirect when a 301 is needed could lead to diminished page authority and a negatively impacted search ranking.
Another common redirect mistake involves creating redirect chains or loops. Redirect chains occur when multiple redirects link sequentially, causing a delay in page loading and potentially losing link equity with each step.
Redirect loops, where a page redirects back to itself or creates an endless cycle, can completely block access to content, frustrating users and search engines alike.
Additionally, failing to update internal links after implementing redirects can also negatively impact SEO performance. Although a redirect is a way to guide users and search engines to the right page, outdated internal links can cause unnecessary redirects, slowing down site navigation and affecting crawl efficiency.
Best Practices for SEO Redirects

Addressing common redirect mistakes can significantly enhance both SEO and user experience, paving the way for effective redirect strategies.
To maintain your website’s SEO, understanding the type of redirect you want to implement is crucial. Whether you choose a 301 or 302 redirect can have different implications for your site’s search engine ranking. A 301 redirect is used for permanent URL changes, ensuring that the SEO value from the original page is transferred to the new location. On the other hand, 302 redirects impact SEO differently, as they are intended for temporary changes and may not pass the same SEO equity.
To ensure best practices for SEO redirects, consider the following guidelines:
- Use a 301 redirect: When the move is permanent, to maintain your website’s SEO authority and search rankings.
- Avoid redirect chains: These can dilute SEO value and lead to slower site performance, negatively affecting user experience.
- Keep an eye on 302 redirects: Use them cautiously, as overuse or misuse can confuse search engines about the page’s final status, impacting SEO.
- Regularly audit redirects: Ensuring all redirects remain relevant and effective, preventing outdated or broken links which can harm your site’s performance.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between 301 and 302 redirects is crucial for maintaining both SEO performance and a positive user experience. While 301 redirects are ideal for permanent URL changes, ensuring the transfer of SEO value and page authority, 302 redirects are better suited for temporary moves, helping preserve the original page’s ranking. Misusing these redirects can lead to significant SEO issues, such as ranking losses and diluted link equity. By carefully choosing the right redirect for each situation, webmasters can avoid common pitfalls, optimize their site’s search visibility, and provide users with a seamless browsing experience.
If you want to ensure your website’s redirects are correctly set up for maximum SEO impact, connect with Syville Gacutan, an experienced SEO Specialist in the Philippines. Syville can help you optimize your site’s redirects, maintain search engine rankings, and enhance user experience. Don’t leave your website’s performance to chance—partner with an expert who understands the importance of proper redirect management.